Cool Tips About How Do You Test A 0 Ohm Resistor

What Is Zero Ohm Resistor ? RayPCB
Zeroing In
1. Understanding the Quirky 0 Ohm Resistor
Ever stumbled upon a component labeled "0 Ohm resistor" and thought, "Wait, what's the point?" You're not alone! These little guys can seem a bit baffling at first. They aren't your typical resistors, designed to impede current flow. Instead, they function more like jumpers or links in a circuit. Think of them as tiny, convenient wires disguised as resistors.
So, why use a 0 Ohm resistor instead of just a wire? Good question! Often, it's about simplifying circuit board design and assembly. They allow for easy component placement using automated machinery, making manufacturing more efficient. They also provide a handy point for making circuit modifications or adding test points later on. Consider them multi-purpose, adaptable circuit elements.
Another reason for their existence relates to pick-and-place machines during PCB assembly. These machines are set up to place resistors. Using a 0 Ohm resistor allows a "wire" connection to be placed using the same process and equipment, rather than requiring a separate wiring step. It's all about streamlining the manufacturing process. Less handling, less cost.
And let's not forget troubleshooting! A 0 Ohm resistor can act as a designated point to easily break a circuit for testing purposes. Simply remove the resistor to isolate a section of the circuit. Re-soldering it back in is a breeze once you're done investigating the fault. It's a lot easier than cutting and splicing wires, that's for sure!
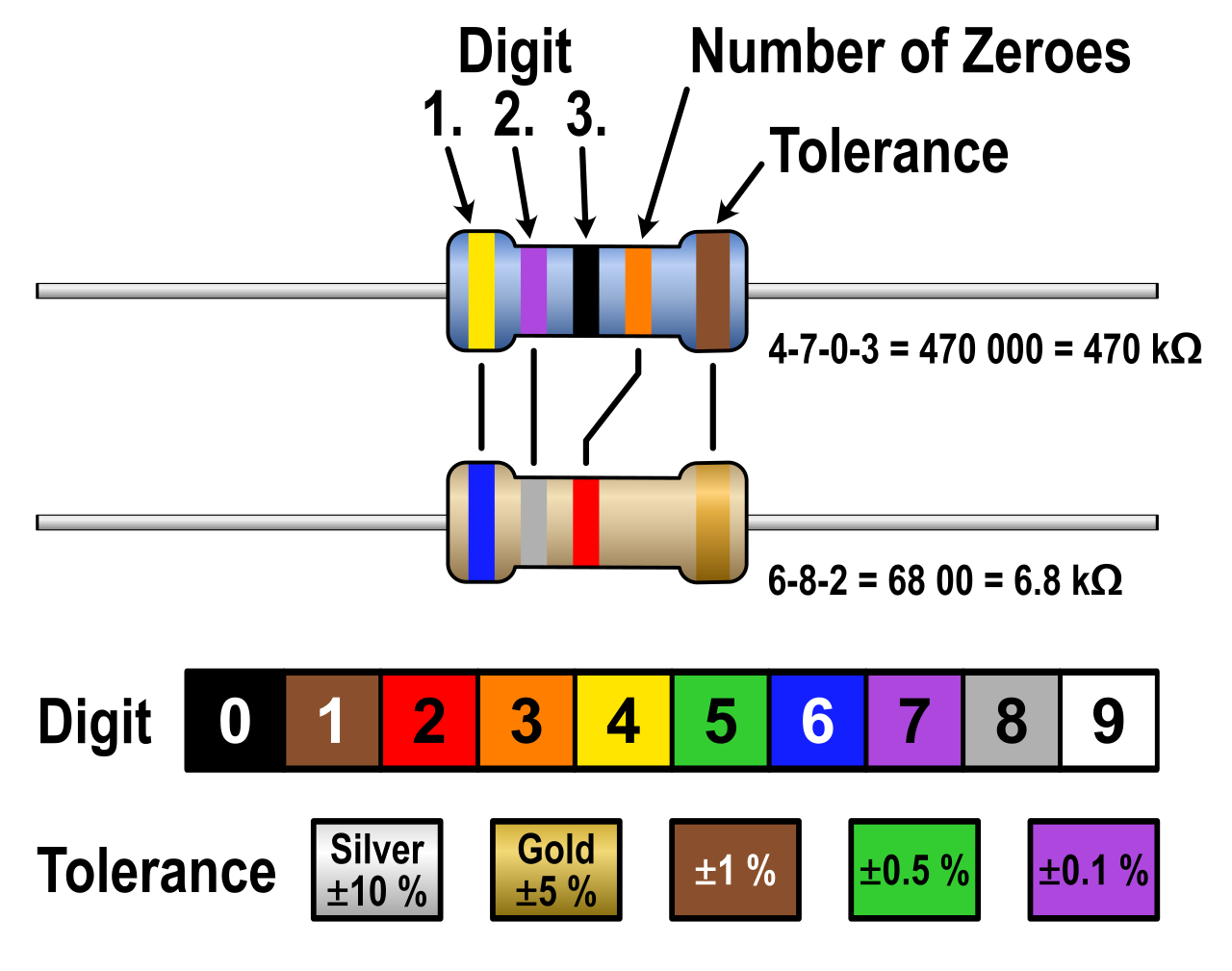
How To Calculate Value Of Resistor Using Color Code A Vrogue.co
The Moment of Truth
2. Putting Your Multimeter to Work
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks — or rather, copper connections. Testing a 0 Ohm resistor is thankfully quite straightforward. You'll need a multimeter, which is an essential tool for any electronics enthusiast. Make sure your multimeter is set to measure resistance, typically indicated by the Omega () symbol.
Now, carefully touch the probes of your multimeter to each end of the resistor. If the resistor is behaving as expected, your multimeter should display a reading very close to 0 Ohms. You might see a tiny fraction of an Ohm, like 0.1 or 0.2 Ohms. This is normal, due to the inherent resistance of the leads and connections.
If you're getting a reading significantly higher than 0 Ohms, say several Ohms or even kilo-Ohms, it suggests the resistor might be faulty or damaged. Perhaps a break in the conductive path inside. In such cases, it's best to replace it with a new one. They're inexpensive, after all.
Conversely, if your multimeter displays "OL" or "Overload," this usually indicates an open circuit. It is as if there is no resistor there at all. This might sound counterintuitive, since a 0 Ohm resistor is supposed to act like a short circuit. However, the "OL" reading means there's a break in the circuit, meaning no current can flow, even through a supposed "short".
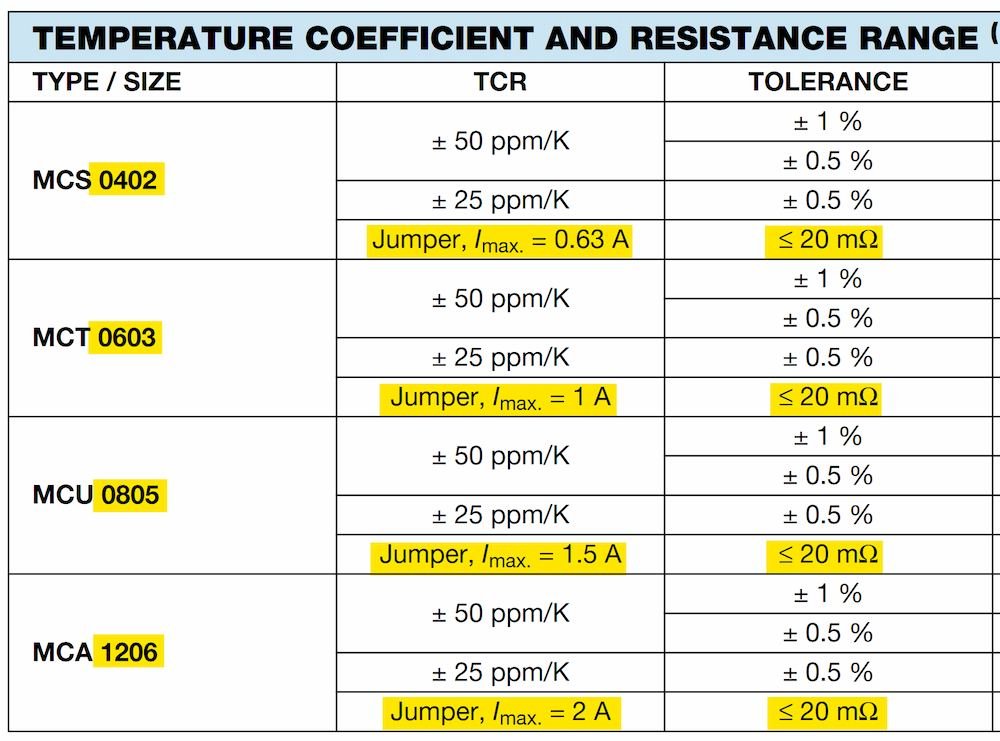
What Is Zero Resistor At Karen Evans Blog
Why It Matters
3. Decoding the Multimeter's Message
So, you've got a reading — now what? Understanding what that reading tells you about the resistor's health is key. A near-zero Ohm reading confirms the resistor is functioning as intended, providing a low-resistance path for current to flow. This is precisely what you want.
A high resistance reading (anything above a small fraction of an Ohm) points to a problem. The resistor may be partially or completely failing, preventing current from flowing properly. This could disrupt the circuit's intended operation, leading to malfunctions or unexpected behavior.
The "OL" or "Overload" reading signifies a complete failure. The circuit is broken at the location of the resistor. This essentially means there's no connection being made, rendering the "jumper" function useless. In this scenario, the resistor needs replacing immediately to restore the circuit's integrity.
It's also a good idea to visually inspect the resistor for any signs of damage, such as cracks, burns, or discoloration. These are telltale signs of a component that's seen better days. Remember, even though they're meant to handle current, excessive heat or voltage can still cause them to fail. Like all components, they have limits!

Beyond the Basics
4. Accounting for Variables in Your Measurements
While testing a 0 Ohm resistor is generally straightforward, a few factors can influence your readings. The accuracy of your multimeter plays a role. Cheaper multimeters may have slightly higher internal resistance, which can affect the precision of your measurements, especially at such low values.
The quality of your test leads can also impact your readings. Old or damaged leads may have increased resistance, skewing the results. Ensure your leads are in good condition and making solid contact with the resistor terminals.
Even the surrounding environment can have a minor effect. Extreme temperatures can slightly alter the resistance of components, although this is usually negligible for 0 Ohm resistors. However, it's always good to be aware of potential influencing factors.
Finally, consider the placement of the resistor in the circuit. If other components are connected in parallel with the resistor, they can affect the overall resistance you measure. For the most accurate reading, it's often best to isolate the resistor from the rest of the circuit during testing. This eliminates any potential interference from surrounding components.
When to Suspect a Problem
5. Identifying Potential Issues
So, when should you even bother testing a 0 Ohm resistor? Well, if you're experiencing unexplained circuit malfunctions, especially in areas where the resistor is acting as a jumper, it's worth checking. Symptoms like intermittent connections, unexpected voltage drops, or complete circuit failures can all point to a faulty 0 Ohm resistor.
Also, if you've recently made modifications to a circuit or if the circuit has been exposed to excessive heat or voltage, it's wise to test the 0 Ohm resistors. These events can stress the components and potentially lead to failures, even in seemingly simple parts like these.
Furthermore, if you're working with older circuit boards, it's a good practice to check the 0 Ohm resistors as part of your routine maintenance. Over time, components can degrade due to age and environmental factors. Early detection of potential problems can prevent future headaches.
And finally, if you are replacing other components in a circuit, test any 0 Ohm resistors nearby as part of a system to ensure the entire circuit is working as expected. If the original component failed due to an issue elsewhere in the circuit, the 0 Ohm resistor might have been affected.

FAQ
6. Q
A: Not in the real world. Every conductor has some minute resistance. A "0 Ohm resistor" just has extremely low resistance, close enough to zero for practical purposes. Your multimeter will likely show something like 0.1 or 0.2 Ohms.
7. Q
A: Often, it's about manufacturing efficiency. Pick-and-place machines are designed to place resistors. Using a 0 Ohm resistor allows a "wire" connection to be placed using the same automated process, streamlining production.
8. Q
A: A failed 0 Ohm resistor usually acts like an open circuit, breaking the connection it's meant to provide. This can lead to circuit malfunctions or complete failures, depending on its role in the circuit.